In the realm of women’s health, PCOD, standing for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a prevalent condition that warrants understanding and awareness. Delving into the full form, PCOD represents more than just an acronym; it encapsulates a range of challenges affecting women’s reproductive health. Let’s embark on a journey to comprehend the meaning and significance of PCOD, exploring its complexities and implications.
PCOD Full Form Unveiled PCOD, the abbreviated form of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, hints at the intricate nature of this hormonal disorder. It involves the ovaries and is characterized by the presence of small cysts, impacting the regularity of the menstrual cycle and often leading to fertility issues. Beyond its acronym, PCOD encompasses a spectrum of symptoms that can vary in intensity and manifestation.
What is PCOD? Understanding PCOD involves recognizing it as a multifaceted health concern rather than a mere acronym. PCOD involves an imbalance in reproductive hormones, particularly insulin and androgens, which can result in irregular periods, cyst formation on the ovaries, and other associated challenges. It’s not just a medical condition; it’s a journey that many women navigate, seeking insights and effective management strategies.
Common PCOD Problems
PCOD introduces a spectrum of issues that can impact various aspects of a woman’s health. From irregular menstrual cycles to fertility concerns, PCOD’s influence is far-reaching. Exploring these common problems provides a comprehensive view of the challenges women may encounter, fostering awareness and proactive health management.
PCOD Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of PCOD is crucial for early detection and effective management. These symptoms encompass irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, acne, and more. By understanding the subtle and not-so-subtle signs, women can take proactive steps towards seeking medical advice, personalized treatment, and adopting lifestyle changes for improved well-being.
PCOD vs PCOS: Unraveling the Differences
In the realm of women’s health, PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disorder) and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) stand as enigmatic conditions that affect many. Let’s embark on a journey to understand each term individually and then explore the distinctions between them.
Understanding PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disorder) PCOD, an acronym for Polycystic Ovary Disorder, is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of small cysts on the ovaries, resulting from an imbalance in reproductive hormones. PCOD can manifest in various ways, impacting menstrual cycles, fertility, and even metabolism.
Cracking the Code of PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) On the other hand, PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a broader and more complex condition. It encompasses not only ovarian cysts but also other metabolic and hormonal disturbances. PCOS often involves insulin resistance, leading to elevated insulin levels, which, in turn, can trigger increased androgen production. This hormonal imbalance can cause irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and excess hair growth.
Comparative Analysis: Navigating the Differences While both PCOD and PCOS share commonalities, such as irregular periods and ovarian cysts, the nuances set them apart. PCOS involves additional metabolic aspects, making it a syndrome rather than a straightforward disorder. This comparative analysis aims to unravel the distinctions, empowering individuals to understand their specific health challenges and engage in informed discussions with healthcare professionals.
PCOD Mysteries: Risk Factors and Causes
The emergence of Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) is influenced by a myriad of factors, contributing to the complexity of this common women’s health condition. Let’s delve into the intricacies of PCOD, exploring the various risk factors and causes that play a role in its development.
Genetic Predisposition: The Family Connection One significant factor in the development of PCOD is genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of PCOD are more likely to experience this hormonal disorder. Understanding one’s family medical history can offer valuable insights into the potential risk of PCOD.
Insulin Resistance: The Metabolic Link Insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, is a key player in PCOD. Elevated insulin levels contribute to increased androgen production, disrupting the normal hormonal balance. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet and sedentary habits can exacerbate insulin resistance.
Hormonal Imbalance: Disruptions in Reproductive Hormones PCOD is fundamentally a hormonal disorder, characterized by imbalances in reproductive hormones. Elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and insulin, along with increased androgen production, contribute to the development of ovarian cysts and menstrual irregularities.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences: The Modern Conundrum Modern lifestyles and environmental factors also play a role in the prevalence of PCOD. Stress, exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, and unhealthy dietary patterns can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, contributing to the manifestation of PCOD.
Understanding the Puzzle: Seeking Solutions This exploration into the risk factors and causes of PCOD aims to demystify the intricate web surrounding this condition. By understanding these contributing elements, individuals can proactively address potential risk factors and work towards promoting hormonal balance and overall well-being.
Deciphering PCOD: Diagnosis and Medical Tests
Understanding and diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) is a crucial step in managing this complex hormonal condition. Let’s unravel the diagnostic process and common medical tests associated with PCOD, providing insights into the identification and assessment of this prevalent women’s health issue.
Clinical Evaluation: Unraveling Symptoms and Medical History The journey to a PCOD diagnosis often begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. Healthcare professionals delve into the patient’s medical history, examining symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, and hirsutism. A comprehensive understanding of the individual’s health background lays the foundation for effective diagnosis.
Hormonal Blood Tests: Assessing Reproductive Hormones Blood tests play a pivotal role in diagnosing PCOD, focusing on hormonal levels. Key hormones, including luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, and insulin, are analyzed. Elevated levels of androgens and disruptions in the LH-to-FSH ratio are indicative of hormonal imbalances associated with PCOD.
Ultrasound Imaging: Visualizing Ovarian Morphology Transvaginal ultrasound is a common imaging technique employed to visualize the ovaries and assess their morphology. The presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, often referred to as “cysts,” is a characteristic feature of PCOD. Imaging studies help confirm the structural aspects associated with PCOD.
Glucose Tolerance Test: Evaluating Insulin Resistance Given the link between insulin resistance and PCOD, a glucose tolerance test may be conducted. This test assesses how efficiently the body processes glucose. Elevated blood sugar levels post-consumption of glucose may indicate insulin resistance, a contributing factor to PCOD.
Thyroid Function Tests: Exploring Hormonal Harmony Thyroid function is intricately connected to reproductive hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) levels are evaluated to rule out thyroid disorders, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of hormonal balance.
Harmony in Health: Lifestyle and Dietary Management for PCOD
Navigating the complexities of Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) involves a holistic approach that extends beyond medical interventions. Lifestyle and dietary adjustments play a pivotal role in managing PCOD symptoms and promoting overall well-being. Let’s explore the key aspects of lifestyle changes and dietary recommendations tailored for individuals grappling with PCOD.
Embracing an Active Lifestyle: Exercise and PCOD Physical activity emerges as a cornerstone in PCOD management. Regular exercise aids in weight management, improves insulin sensitivity, and helps regulate menstrual cycles. Whether it’s brisk walking, jogging, yoga, or other forms of exercise, incorporating a routine that suits individual preferences can significantly contribute to overall health.
Balanced Nutrition: A Dietary Blueprint for PCOD Dietary choices wield considerable influence over PCOD symptoms. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet can help regulate hormonal imbalances and manage weight. Key dietary recommendations for individuals with PCOD include:
Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. These nutrient-rich foods provide essential vitamins and minerals.
Mindful Carbohydrate Consumption: Opt for complex carbohydrates over refined ones. Managing carbohydrate intake can assist in stabilizing blood sugar levels.
Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats support hormonal balance.
Protein-Rich Diet: Include adequate protein from sources like lean meats, legumes, and dairy. Protein plays a role in satiety and muscle health.
Hydration Matters: Stay well-hydrated with water and herbal teas. Hydration supports overall health and can aid in weight management.
Stress Management: A Holistic Approach Chronic stress can exacerbate PCOD symptoms. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness contribute to stress reduction. Prioritizing adequate sleep also forms an integral part of stress management.
Individualized Approach: Consulting Healthcare Professionals While general recommendations offer valuable guidelines, it’s crucial to recognize the individuality of PCOD experiences. Consulting healthcare professionals, including dietitians, endocrinologists, and gynecologists, ensures personalized guidance tailored to specific health needs.
By embracing a lifestyle that intertwines physical activity, mindful nutrition, and stress management, individuals with PCOD can foster a harmonious relationship with their well-being. This holistic approach not only addresses immediate concerns but sets the stage for sustained health and vitality.
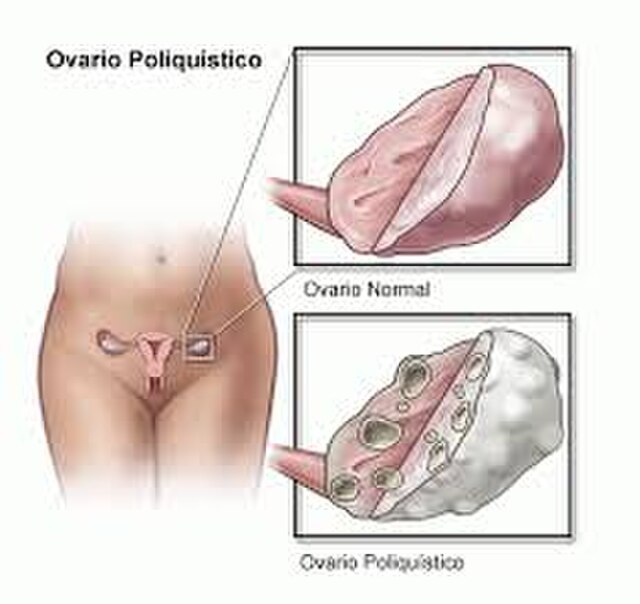
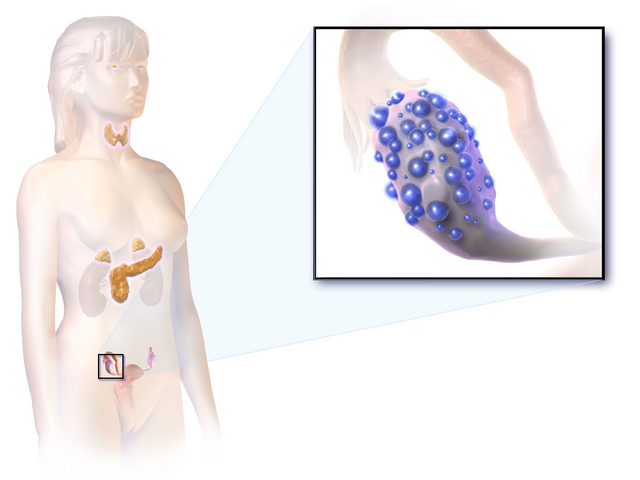
Navigating Solutions: Treatment Options for PCOD
Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) requires a multifaceted approach to management, involving both conventional medical interventions and complementary therapies. Understanding the diverse treatment options available empowers individuals to make informed decisions based on their unique health needs.
1. Medical Interventions: Addressing Hormonal Imbalances Medical treatments for PCOD often focus on alleviating hormonal imbalances and managing specific symptoms. Key interventions include:
- Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and control androgen levels.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: Medications like spironolactone may be recommended to address symptoms related to elevated androgen levels, such as acne and hirsutism.
- Metformin: This medication is prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity, helping manage associated metabolic issues.
2. Lifestyle Modifications: An Integral Component While medications target specific aspects of PCOD, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in overall management. Embracing a healthy lifestyle involves maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction practices.
3. Alternative Therapies: Complementary Approaches Complementary therapies offer additional avenues for managing PCOD symptoms and enhancing overall well-being. These may include:
- Acupuncture: Some individuals find acupuncture beneficial for regulating menstrual cycles and reducing stress.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, like spearmint and chasteberry, are explored for their potential in managing PCOD symptoms.
4. Fertility Treatments: Addressing Reproductive Concerns For individuals facing fertility challenges due to PCOD, fertility treatments such as ovulation induction or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be considered. Consulting with a reproductive endocrinologist provides insights into personalized fertility options.
5. Collaborative Care: Consulting Healthcare Professionals PCOD management is most effective when approached collaboratively. Consulting with a healthcare team comprising gynecologists, endocrinologists, nutritionists, and mental health professionals ensures a comprehensive and tailored strategy.
Understanding the array of treatment options empowers individuals to actively participate in their PCOD management journey. Combining medical guidance with lifestyle adjustments and complementary therapies fosters a holistic approach that addresses the diverse facets of PCOD, promoting long-term well-being.
Navigating Puberty: PCOD in Adolescents
Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) can manifest during adolescence, presenting unique challenges and considerations for young individuals undergoing puberty. Understanding PCOD in this demographic is crucial for timely intervention and support.
Early Recognition and Diagnosis: PCOD in adolescents may exhibit distinct symptoms, such as irregular periods, acne, or excessive hair growth. Early recognition and diagnosis are essential for proactive management.
Hormonal Changes and Puberty: The hormonal fluctuations associated with puberty can exacerbate PCOD symptoms. Increased androgen levels may contribute to acne, oily skin, and irregular menstrual cycles during this developmental stage.
Impact on Menstrual Health: Adolescents with PCOD may experience irregular or absent periods, which can be emotionally challenging. Educating young individuals about menstrual health and providing support is crucial for their overall well-being.
Nutritional Guidance: Dietary habits established during adolescence can significantly impact PCOD management. Offering nutritional guidance that emphasizes balanced meals, adequate hydration, and healthy lifestyle choices is paramount.
Psychosocial Support: Dealing with PCOD in adolescence involves navigating physical and emotional changes. Psychosocial support, including open communication, counseling, and peer interactions, plays a vital role in fostering resilience.
Educational Initiatives: Implementing educational programs in schools and healthcare settings helps raise awareness about PCOD in adolescents. Providing age-appropriate information equips young individuals with the knowledge to manage their health proactively.
Collaborative Care: The management of adolescent PCOD often requires collaboration between pediatricians, gynecologists, nutritionists, and mental health professionals. A multidisciplinary approach ensures comprehensive care tailored to the unique needs of adolescents.
Addressing PCOD in adolescents involves not only medical interventions but also holistic support that considers the emotional and social aspects of development. By fostering awareness, providing education, and offering a collaborative healthcare approach, we empower young individuals to navigate PCOD with resilience and confidence.