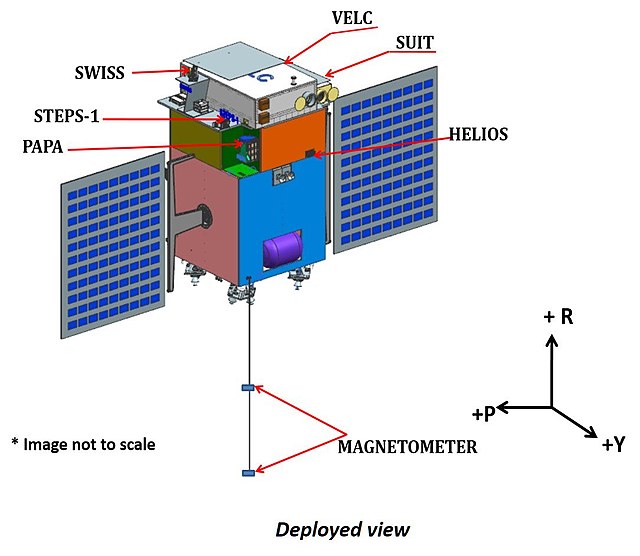
The Aditya-L1 mission, India’s ambitious venture into solar study, is poised to be a significant milestone in the nation’s space exploration endeavors. It carries a suite of seven distinct payloads, each meticulously designed and developed to unravel the mysteries of our nearest star, the Sun. Aditya-L1’s Payloads are categorized into two main types: Remote Sensing Payloads and In-situ Payloads, each serving a unique purpose and collectively contributing to our comprehensive understanding of the Sun’s behavior and dynamics.
Remote Sensing Payloads:
1. Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC):
- Capability: Corona/Imaging & Spectroscopy
VELC is a groundbreaking instrument designed to observe the Sun’s outermost layer, the corona, with remarkable precision. By capturing visible emission lines from the corona, VELC provides critical insights into the dynamics and structure of this enigmatic region. It combines imaging and spectroscopy techniques to decode the secrets of the Sun’s corona.
2. Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT):
- Capability: Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging – Narrow & Broadband
SUIT is tasked with the challenging mission of capturing high-resolution images of the Sun’s photosphere and chromosphere. It employs both narrow and broadband filters to analyze specific wavelengths of solar ultraviolet radiation, allowing scientists to study the Sun’s surface features and magnetic activities in detail.
3. Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS):
- Capability: Soft X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation
SoLEXS specializes in detecting soft X-rays emitted by the Sun. This instrument observes the Sun as a star, studying its X-ray emissions to gain insights into its composition, temperature, and other critical parameters. By focusing on the Sun’s X-ray spectrum, SoLEXS enhances our knowledge of its physical properties.
4. High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS):
- Capability: Hard X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation
HEL1OS complements SoLEXS by observing hard X-rays from the Sun. It provides detailed spectroscopic information about the Sun’s X-ray emissions, aiding in the understanding of its high-energy processes. Together with SoLEXS, HEL1OS contributes to Sun-as-a-star observations, which are essential for studying the Sun’s fundamental characteristics.
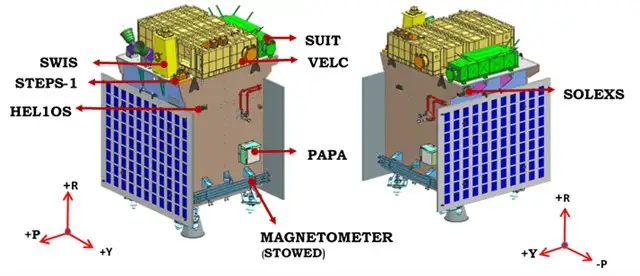
In-situ Payloads:
5. Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX):
- Capability: Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Protons & Heavier Ions with directions
ASPEX plays a crucial role in studying the solar wind and the particles it carries. By analyzing protons and heavier ions and their directions, ASPEX helps us comprehend the nature and behavior of the solar wind, shedding light on its impact on space weather and Earth.
6. Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya (PAPA):
- Capability: Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Electrons & Heavier Ions with directions
PAPA, like ASPEX, focuses on the solar wind but extends its analysis to electrons and heavier ions. By providing data on these particles and their directions, PAPA contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the solar wind’s composition and dynamics.
7. Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers:
- Capability: In-situ magnetic field (Bx, By, and Bz)
These tri-axial digital magnetometers play a pivotal role in measuring the Sun’s magnetic field in three dimensions: Bx, By, and Bz. This information is critical for understanding the Sun’s magnetic behavior and its influence on space weather and solar phenomena.
The Aditya-L1 mission is a testament to India’s technological prowess and commitment to advancing space science. Through these meticulously crafted payloads, the mission aims to explore the Sun as a star, unveil the mysteries of its outer atmosphere and magnetic activities, and contribute significantly to our knowledge of solar phenomena. With each payload serving a specific purpose, the collective data obtained promises to revolutionize our understanding of the Sun’s behavior and its impact on our solar system, ultimately enhancing our ability to predict and mitigate space weather-related challenges here on Earth.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Read Our Other Related Articles